ECS Eddy current separator
An eddy current separator is a dual pulley conveyor system, where the non-metallic rotor cover houses an independently rotating high-speed magnetic rotor. Separation occurs when a non-ferrous metal particle (e. g. aluminium, copper or zinc) gets into the magnetic zone. The non-ferrous metal particle is exposed to rapidly changing magnetic polarity. This induces ‘eddy currents’ into the particle generating an electrical current that subsequently creates its own magnetic field. The two magnetic fields oppose against each other and cause the repulsion of the non-ferrous metal particle
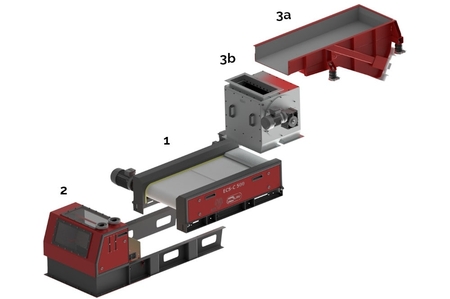
Design of the non-ferrous metal separator ECS
Eddy current separator ECS made by SOLLAU consists of three modules:
- Module No. 1 (equipped with a magnetic rotor)
It is the only standard module supplied. In its driven cylinder there is a strong magnetic rotor (the rotor shell is made of fiberglass). - Feeding module (No. 3a / 3b)
This input module is supplied as an optional accessory, taking care of pre-cleaning and the correct and even distribution of the processed material on the conveyor belt. Therefore, this segment may be fitted, e. g. with a magnetic drum (3b), a magnetic pulley MV, an overband magnet DND-AC (for separation of ferrous particles) and/or a vibrating feeder (3a). - Sorting module (No. 2)
The final segment is used for more precise sorting of already separated materials. The final sorting module (2) consist of a closed box with a material divider that can be set according to the magnetic characteristics of the materials being cleaned at that particular moment (in order to separate the metal particles from the inert ones in the optimal way).
Except segments 3a, 3b and 2, we also offer a control box with a PLC control unit, LCD monitor, etc. as optional accessory.
Prerequisites for optimal application of eddy current separators
The magnetic field range of these separators is relatively short. Therefore, the basic conditions for the separation of non-ferrous metals include the formation of a uniform and the lowest possible layer of the material on the separator belt (the layer height should not exceed the maximum material size, if feasible it should be a monolayer). That is also the reason why the material should be thoroughly loosened (e. g. by a vibrating feeder).
The magnetic field of the centrically mounted magnetic rotors is very strong also in the bottom part of the conveyor pulley. That is why sometimes it keeps holding ferromagnetic particles and they are not thrown away by the belt movement and can burn in. This subsequently may lead to damage to the conveyor belt, to the non-magnetic rotor housing or even to the rotor itself. Therefore, especially in case of centric versions of eddy current separators, a perfect removal of ferrous contaminants before the entry of the cleaned material into the magnetic field of the non-ferrous metal separator is to be ensured. There are used for this purpose e. g. magnetic drums, magnetic pulley or overband magnets.
Electrical conductivity of materials
The repulsive distance, to which the metal particles are repelled, depends directly on the electrical conductivity and size of the treated particles (and also on their specific weight). Therefore, e. g., pieces of aluminum sheets are easier to separate than short thin copper wires.
Materials which can be easily sorted by ECS
Eddy current separators are especially suitable for sorting of well-conducting light non-ferrous metals (such as copper, aluminum, magnesium, silver, etc.). Objects or particles of brass, zinc, gold, cadmium or tin are more difficult to separate.
Materials unsuitable for the ECS application
Eddy-current separators are not suitable for sorting of heavy or poorly conductive metals (as lead, platinum, titanium, etc.). These are materials with very low conductivity or extremely heavy materials which - despite the strong magnetic field of the rotating magnets - cannot be repelled at the end of the conveyor belt and fall vertically down due to gravitation.